Artist : Mr. Chau-yih Yu
Introduction
Since the first commercial launch of 5G services in 2020 in Taiwan, 5G has presented new challenges for mobile broadband operators. On the one hand, 5G networks are intended to support faster mobile broadband speeds and lower latencies, making new applications possible, such as on-demand video and autonomous vehicles. On the other hand, 5G will require 4G/5G mobile broadband operators to have access to large amounts of spectrum to make these new services a reality. In contrast to the business competition, policymakers (ie, regulators and legislators) are making it a top priority to ensure that the emerging digital industry has the tools it needs to support commercial 5G deployments.
This article provides updates on the actions of the National Communications Commission (NCC) and the Ministry of Digital Affairs (MODA), as well as on congressional efforts, for Taiwan to achieve a leading position in the developing 5G market.
Regulatory actions and initiatives
Business merger and acquisition
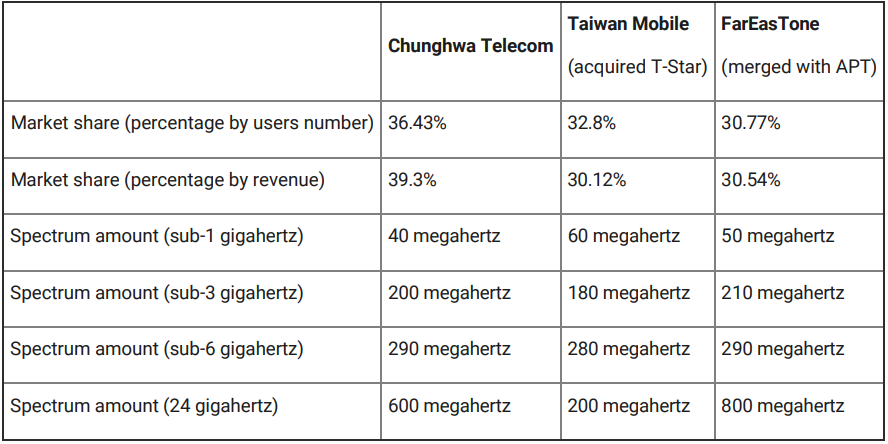
On 2 November 2022, the chairman of the NCC responded to the legislator’s inquiry that his agency expects to conclude its review on two merger-and-acquisition cases within the next three months. Further to the announcement of Taiwan Mobile’s acquisition of T-Star on 31 December 2021 (followed by the FarEasTone merged with Asia Pacific Telecom in February 2022), little progress has been made at the NCC’s review, despite a one-day hearing conducted by the NCC in late September 2022.
The 5G penetration rate hit 25% as of October 2022, with around 5.7 million subscribers nationwide.
If the regulators gave their approval, the 5G market would become an oligopoly in the wireless industry (for further details please see “Telecoms M&A accelerates competition on frequency bands“).
Regulation on 5G vertical application network
On 8 November 2022, the MODA clarified it is in the middle of negotiation with the NCC to finalise a draft regulation of 5G vertical application networks in the designated frequencies of 4.8 gigahertz to 4.9 gigahertz (for further details please see “NCC invites consultation on draft regulation of 5G vertical application network“). This would imply further delay of the private network deployment from the fourth quarter of 2022 to March 2023 at the earliest. It has been widely suspected that there is still a struggle for the transfer of regulatory power between the NCC and the MODA.
On the same day, the MODA shared several success cases of using the 3.5 gigahertz band in application of a manufacturer’s 5G private network under cooperation with existing 5G operators
High-band for mmWave
Starting from 8 November 2022, the MODA has been accepting applications for next-generation satellite communication in designated high-bands. Among these, the 27,500-27,900 megahertz band is a subset of the third-generation partnership project (3GPP) band “n257”, which was offered in the April 2020 5G spectrum auction. Any further proposed use of the satellite systems in the 27,900-29,500 megahertz band must coordinate with the four licensed 5G operators for share-use in this case (for further details please see “MODA releases spectrum for next generation satellite communication“).
All the 5G operators awarded frequency licences of 28 gigahertz band have been silent since 2020 on any possible plan of implementing mmWave-partly due to the high cost of development, but they are probably looking forward to Apple’s further lead in the distribution of the iPhone 5G mmWave version.
5G networks and infrastructure
Government subsidy on 5G networks and infrastructure
As of October 2022, there are a total of 35 government subsidy programmes in relation to 5G deployment in place for policy review. Aside from promoting 5G innovation technology, the government considers it crucial to achieve a high 5G reach on the island over the next three years. The MODA, the Ministry of Education, the National Science and Technology Council, and the Council of Indigenous Peoples are planning for a joint effort to enhance 5G networks and infrastructure in rural areas by 2025 by budgeting 33.95 billion new Taiwan dollars (approximately $1.1 billion) for the subsidy programmes currently being executed.
Open Radio Access Network (Open RAN)
On 14 October 2022, the Industrial Development Bureau (IDB), which is a branch sitting under the Ministry of Economic Affairs, coordinated an exhibit of Taiwanese 5G companies at the 5G Open RAN and AIoT Showcase in the 5G & Smart City Pavilion at the Taiwan Expo USA 2022, held from 12 to 14 October 2022 in Washington, DC. These companies included:
HTC;
QCT;
Ufi Space;
Lions;
Askey;
MTI;
Lite-On;
Compal;
Edgecore; and
TMYTEK.
This showcase demonstrates how Taiwan offers great business potential for US companies, catering to the needs of both public and private networks in the global marketplace.
The United Kingdom has recently also strengthened Taiwan trade ties, as its Trade Policy Minister Greg Hands headed to Taiwan for the first in-person trade talks since the covid-19 pandemic. On 7 November 2022, Greg Hands talked to Taiwan Digital Minister Audrey Tang regarding the collaboration on 5G Open RAN and strengthening 5G supply chain resilience.
Legislative efforts
Tax Incentives proposed for 5G Research and Development
On 17 November 2022, the Executive Yuan (the cabinet) approved a proposal of amendment to the Special Act for Industrial Innovation, which will create further tax incentives to help research and development activities of Taiwanese IC companies and 5G manufacturers that play critical roles in the international supply chain.